Library Construction
Vectors
Biology
Vectors
Vector Ligations
We have developed restriction enzymes as tools allowing us to break the genome up into smaller, more manageable pieces - each with a defined end (the restriction site).
We can separate DNA fragments based on their size (gel electrophoresis).
We can identify specific DNA fragments by hybridization to a defined probe.
Now we have developed vector systems that we can use to propagate individual restriction fragments.
We still need to discuss the joining of vector and foreign DNA restriction fragments
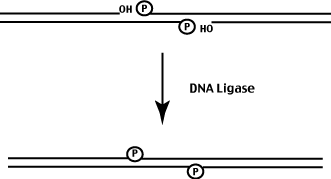
Recall the process of replication. Leading strand synthesis is continuous while Lagging strand synthesis is discontinuous.
Discontinuous synthesis results in short fragments that must be joined together - a reaction catalysed by the enzyme DNA ligase.
Ligase takes the 3' OH from one fragment and covalently joins it to the 5' phosphate of the adjacent fragment.
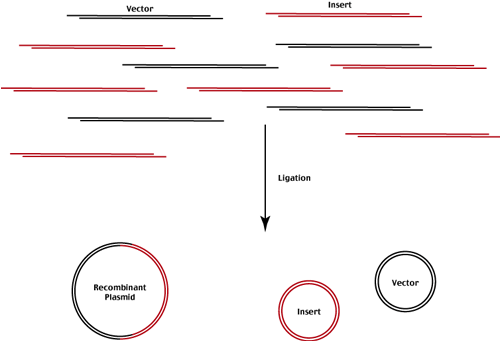
the desired products of ligation are circular DNA molecules composed of both vector and foreign DNA fragments.
These are identified after transformation into the appropriate host
(antibiotic resistant and lac delta-M15).
Only bacteria carrying a plasmid can grow in the presence of the antibiotic (positive selection)
Recombinant plasmids containing an insert are identified by their lacZ- (white in the presence of X-gal).
and lacZ alpha-complementation is
insertionally inactivated
(White)
(antibiotic sensitive)
alpha-complementation
is intact
(Blue)
When working with phage vectors,
the desired ligation product is a long linear DNA molecule containing
a phage genome ligated to an foreign DNA insert ligated to a phage genome ligated to a foreign DNA insert ligated to a phage genome ligated to a foreign DNA insert ligated to a phage genome...
This linear concatemer is the preferred substrate for packaging into phage heads in vitro.
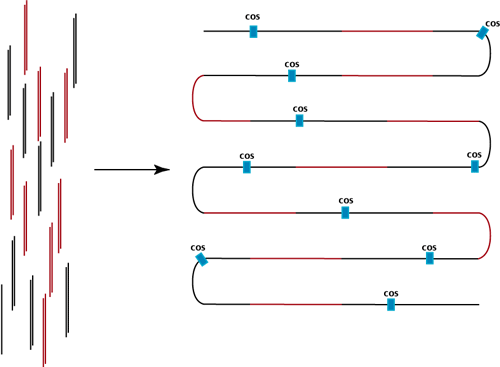
To package these recombinant genomes into viable phage particles, we add empty phage heads and tails to the ligation products.
The phage head binds to a cos site in the linear concatemer,
cuts it to produce one single stranded cos end,
reels in the DNA in between the first cos site and the second, packaging it into the phage head,
and finally cuts the second cos site to produce the other single stranded cos end.
The filled phage head then associates with the phage tail to produce the infectious phage particle.
The recombinant phage produced by this in vitro packaging reaction are then selectively amplified on either
an Hfl strain of E coli (for insertion vectors where the cI gene has been insertionally inactivated)
or
an E. coli strain carrying a P2 lysogen (where the removed stuffer encodes the spi phenotype).