Molecular Genetics
Midterm I Review Questions Page 1
Well, I've finally got a few review questions for you.
Don't fool yourself into thinking that these questions are what you will be facing on your midterm.
These questions are intended to REMIND you
of the topics we have covered and the specific aspects I feel are most important...
You are given an acid hydrolysate of a nucleic acid sample.
What three classes of molecules would you find in the hydrolysate?
Illustrate how these components combine to form the nucleic acid polymers.
Which components would you find if the nucleic acid sample contained only DNA? only RNA?
Describe the chemical characteristics of these Nitrogen Bases.
Be able to RECOGNIZE the structures of A, G, C, T and U.
Why do complementary base pairs form? What holds them together?
5-Br-Uridine is often used to label newly synthesized DNA.
Provide a rationale for why 5-Br-U is incorporated into DNA and not RNA?
double stranded nucleic acids behave more like 'flexible' rods.
Explain.this difference in behaviour.
Provide a rationale for why specific components are found on the 'outside' and 'inside' of the structure.
How does the structure of a double-stranded DNA molecule differ from the structure of an duplex RNA molecule?
Would these two structures differ at all in chemical stability? Provide a rationale for your answer.
Outline the levels of hierarchical packaging of eukaryotic genomic DNA.
Why do we call level 2 - 'beads on a string'?
Draw a picture of a bead.
Put in lots of little details in POINT FORM
Show the path taken by the DNA. How much DNA is there?
What are the most important interactions holding the DNA in the bead.
What/Where is H1?
What interactions are primarily responsible for the formation of this structure?
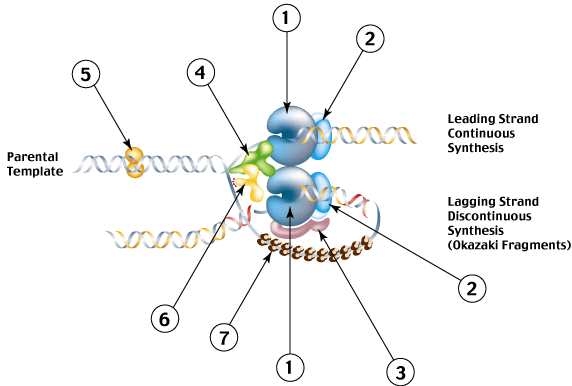
What is responsible for the high fidelity of DNA replication?
Why do we call them leading and lagging strands?
What is an Okazaki fragment?
Review Page 2